All You Need to Know About PREMATURE EJACULATION
- Admin

- Jun 10, 2021
- 4 min read
Updated: Jun 17, 2022

What is Premature Ejaculation (PE)?
The ejection of sperm from the body is known as ejaculation. Premature Ejaculation has been explained in a variety of ways. In general, PE is when ejaculation occurs earlier than a man or his partner prefers during intercourse.
Premature ejaculation is a male sexual disorder in which ejaculation occurs with minimal stimulation, before or nearly before vaginal penetration, usually within one minute. It is described as inability to withhold ejaculation on all or nearly all vaginal penetrations causing negative personal effects such as anxiety, bother, irritation, and/or aversion to sexual intimacy.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is not the same as PE. The failure to obtain and sustain an erection that makes for a pleasurable sexual experience is referred to as ED. PE, on the other hand, may occur in conjunction with ED.
PE may or may not be a cause for concern. It can be aggravating if it makes sex less pleasurable and has a negative effect on relationships.
PE can make you feel as though you've lost some of the intimacy you once had with a sexual partner. You can become enraged, embarrassed, or offended, and withdraw from your partner. PE may also cause partners to feel betrayed or disconnected.
You may want to consult a doctor if PE:
is occurring or has happened frequently enough to trigger relationship issues
makes you feel self-conscious
prevents you from pursuing intimate relationships
How does ejaculation occur?
The central nervous system is in control of ejaculation. Signals are sent to the spinal cord and brain when men are sexually aroused. Upon reaching a certain level of excitement, the signals are transmitted from the brain back to the reproductive organs resulting in semen being ejected through the penis (ejaculation).
There are two phases in ejaculation:
Phase 1: Emission
Sperm from the testicles travels to the prostate and combines with seminal fluid to form semen. The vasa deferentia are tubes that aid in the movement of sperm from the testicles to the base of the penis.
Phase 2: Expulsion
Contraction of the muscles at the base of the penis causes the sperm to be forced out of the penis. Ejaculation and orgasm (climax) usually occur at the same time. Some men climax without ejaculating. Erections usually disappear after this stage.

What are the symptoms of PE?
PE episodes that occur occasionally are normally not a cause for concern. If PE happens excessively or for a prolonged period of time, you may require intervention.
The failure to withhold ejaculation for more than a minute after penetration during intercourse is the most classic condition of PE. For some people, rapid orgasm during masturbation may also be a concern.
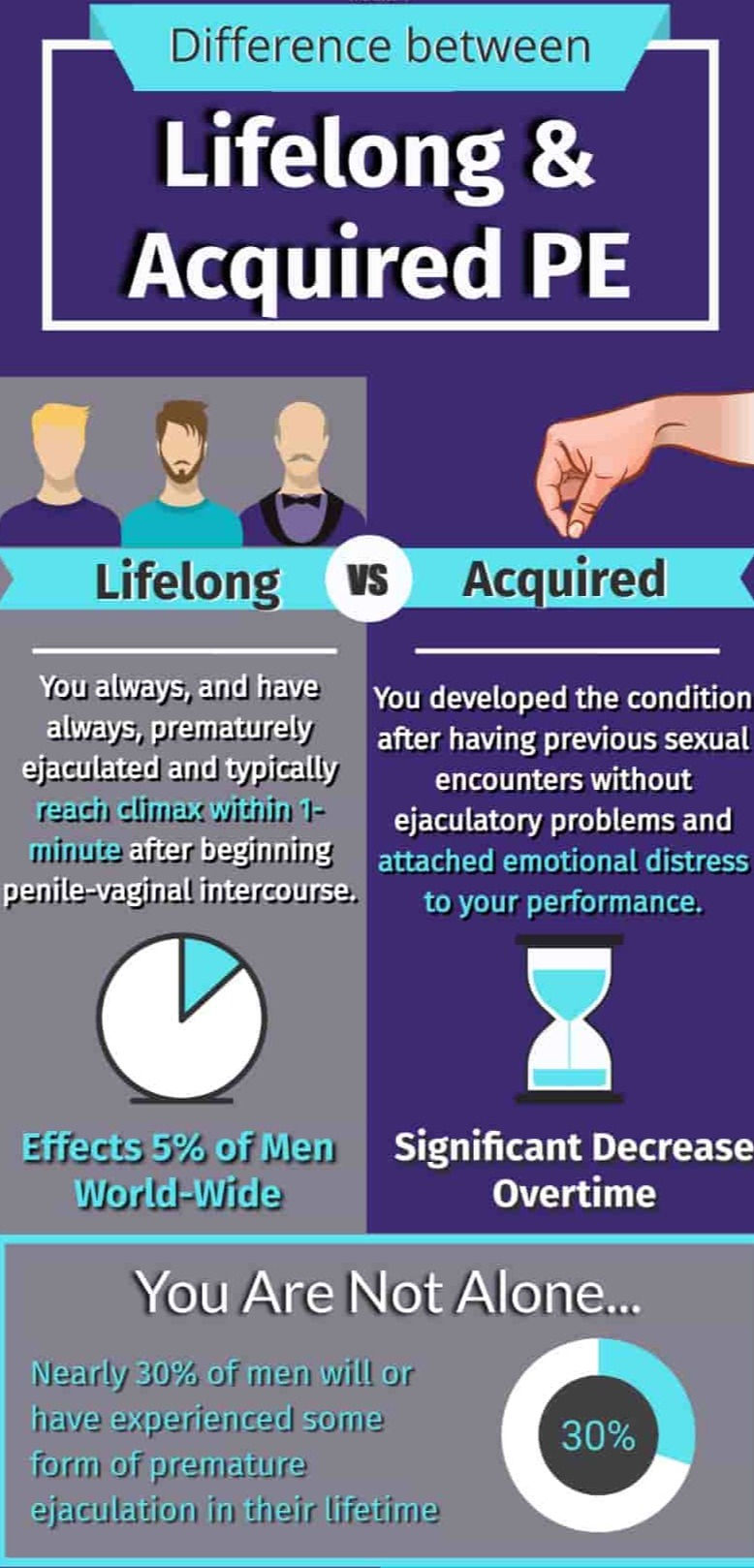
PE can be classified into lifelong or acquired:
Lifelong (primary) PE: since your first sexual encounter, you've had this issue every time or almost every time.
Acquired (secondary) PE: you've had ejaculations that lasted longer in the past, but you've developed PE recently.
Causes of PE
This sexual dysfunction can be cause by a variety of factors, including:
1) Physiological and physical factors
Serotonin may play a role in PE, but the exact cause is unknown. Serotonin is a natural substance produced by nerves in your body. Serotonin levels in the brain increase the time it takes to ejaculate. Low doses can trigger PE by shortening the time it takes to ejaculate.
Psychological
Most psychological aspects may be transient. For example, an individual may have had PE during their first sexual encounters, but as they grew older and had more sexual encounters, they developed ways to delay ejaculation. Common psychological factors that can cause PE are depression, anxiety, stress, lack of confidence, unrealistic expectations about performance in sex or dissatisfaction in current relationship.
Pathological
PE may be caused by abnormal levels of certain hormones, such as testosterone. Inflammation of the prostate or urethra can also cause symptoms like PE and ED.
PE also has no well-documented risk factors, and it can strike anyone at any age. While ageing causes changes in erections and ejaculation, it is not a direct cause of PE. Erections cannot be as firm or as large in older men. It's possible that erections won't last as long before ejaculation. It is also likely that the sensation of impending ejaculation would be shorter. An older man can ejaculate earlier as a result of these changes.
How to diagnose PE
You may begin by consulting a primary care physician or a urologist. A urologist is a medical professional in male sexual function and urinary system health. Usually, your doctor will take a thorough history from you before proceeding with a physical examination. Some of the questions that may be asked are:
How often does it happen?
Length of time before ejaculation?
How long have you had the issue?
Does it happen with just one partner, or all?
Does it happen with every attempt of sexual activity?
Types of sexual activity you and your partner take part in and their frequency
How has PE changed your sexual activity?
Are there any other factors that can make PE worse or better (i.e., drugs, alcohol, etc.)?
Different diagnostic methods and questionnaires have been developed to classify patients with PE due to the various definitions given to the condition. Premature ejaculation profile (PEP) and premature ejaculation diagnostic tool (PEDT) are two examples of them.
A physical examination, including assessments of the vascular, endocrine, and neurological systems, as well as appropriate laboratory tests, are also required.
How We Approach to help You Overcome PE Issue?
Click on the picture to know more
Come and visit our men's health clinic in Kuala Lumpur




Comments